Great River Energy (GRE), a not-for-profit electric cooperative serving Minnesota and parts of the Midwest, provides reliable and affordable energy to more than 700,000 people. As a cooperative owned by its members, the organization is deeply committed to operational excellence, environmental stewardship, and community service. In an industry rapidly evolving with new technologies and increasing demands for efficiency, Great River Energy continues to stay ahead by investing in innovative tools and strategies.
A recognized leader in applying geographic information system (GIS) technology, GRE has embraced Esri solutions to transform how it manages infrastructure, responds to emergencies, and plans for the future. GRE’s forward-thinking use of spatial data empowers teams across the organization, enabling smarter decisions and stronger connections with the communities it serves.
CHALLENGE
Ten years ago, GRE faced an operational challenge with its traditional fault location process. System operators relied on measuring on the screen in GIS to estimate the location of a fault along the transmission lines. This method required measuring these distances based on predictive relay data from the EMS historian and manual measuring tools in the GIS system. This worked well for many years, but operators were looking to automate this process to locate the fault locations faster, more accurately, and have the ability to correlate lightning strike data into it to help identify causes for momentary outage.
“System operations approached the GIS department and asked if there was a way we could help improve the efficiency of their fault location process, as the current process was kind of cumbersome and time-consuming. So we put our heads together to come up with a solution.” Jeff Grussing, Manager of GIS Development and Technology at GRE.
Staff from system operation and GIS departments met and identified the tools and data that could be used to create an automated solution.
SOLUTION
To address the inefficiencies of manual fault location, GRE implemented a GIS-based solution that automated the entire process. By leveraging linear referencing, also known as measured routes, the new system can accurately trace and display the fault locations on the transmission system based on the relay data. It also incorporates lightning strike data from the weather provider to help identify possible causes of momentary outages.
GRE’s IT development staff developed a custom widget and server object extensions that integrate the organization’s EMS data historian and GIS, enabling near real-time access to relay information. Now, when a fault occurs, the GIS tool quickly interprets the relay data and traces to the distance provided, then visually marks the probable fault location on a digital map. This enables system operators to quickly direct crews to precise locations without relying on manual measurement. The result is a faster, more accurate response that saves time, reduces operational costs, and improves customer reliability.
“Leveraging GIS’s many capabilities, we were able to automate multiple processes, including capturing data directly from the EMS historian, providing precise fault locations, and correlating lightning data. The GIS application enabled rapid decision making.” Mark Peterson, Director of System Operations at GRE
The system also stores the fault locations and lightning strike data for future analysis. Furthermore, fault locations, whether sustained or not, can be displayed in ArcGIS Field Maps for use by mobile workers to navigate to the fault location.
RESULT
The implementation of the GIS-based fault location tool delivered immediate, measurable improvements at GRE. A significant result was a substantial reduction in the time system operators spent analyzing faults. With real-time relay data feeding directly into the GIS, operators no longer needed to rely on digital measuring tools. Fault locations can be identified and visualized within seconds, enabling faster crew dispatch and shorter response times. Additionally, the tool enhanced data accuracy, reducing the margin for error in fault estimation and improving the overall reliability of the process. Finally, since the fault data and fault location data are stored, GRE can provide crisper, more precise analysis of the causes of faults for better asset health.
BENEFIT
The GIS-enabled fault location solution delivered benefits across GRE’s operations. It enables the ability to provide field crews with timely, accurate fault information and provides a data source for post-storm analysis.
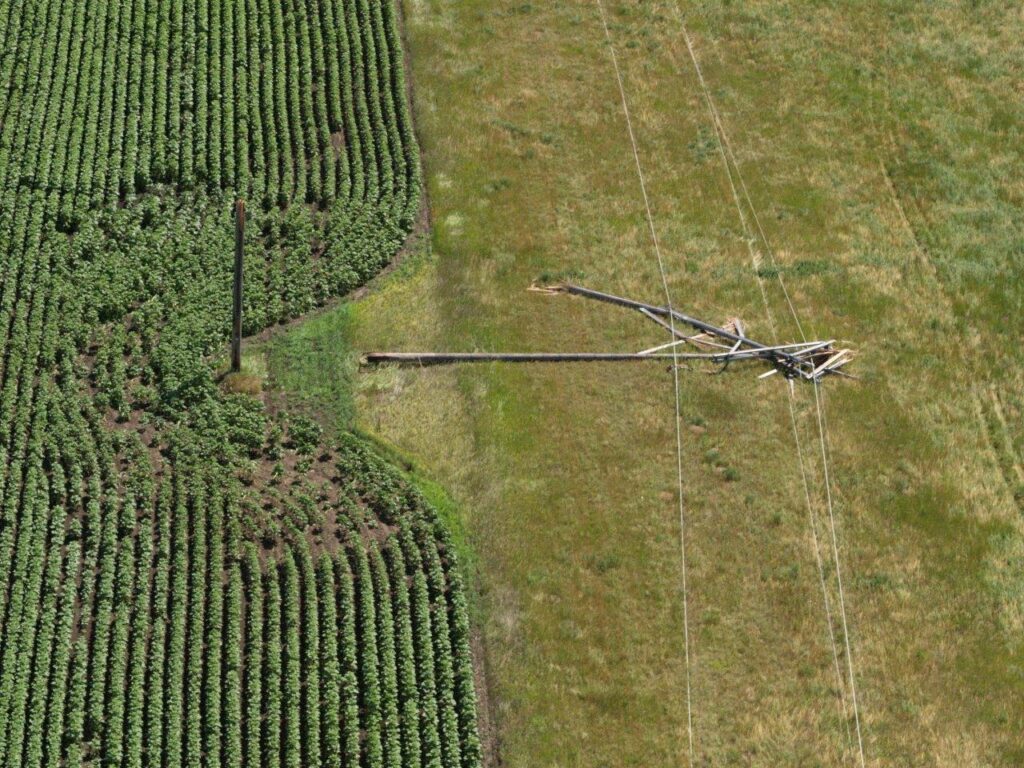

GRE leverages GIS to discover the location of damaged equipment.
By integrating with Esri’s mobile tools, such as ArcGIS Field Maps, and utilizing feature services, operators can now store and share fault locations seamlessly. If a line experiences a non-momentary or sustained fault, the system logs that location and syncs it across all platforms, providing field crews with a precise target. Real-time updates within ±10 seconds of a relay event also enable the system to overlay relevant environmental data, such as lightning strikes, helping crews determine the likely cause of the fault.
“The GRE GIS fault tracing tool gives me precise fault locations down to the structure number. Isolation can be done within minutes with motor-operated switches, restoring customers quickly and efficiently. Lineworkers are dispatched directly to the reported trouble area and can quickly identify the issue and begin repair activities.”-Marshall Brown, System Operator
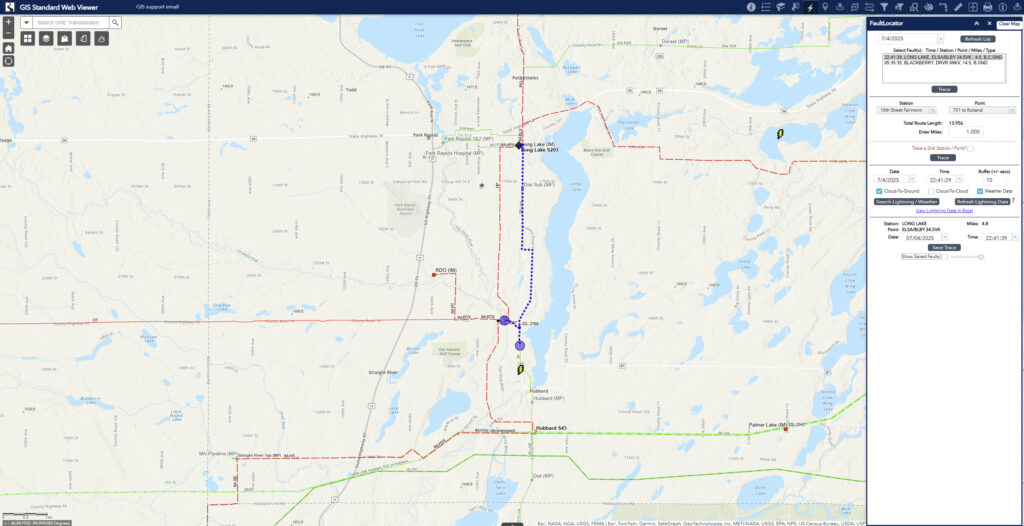
GRE uses GIS to route crews to potentially damaged transmission equipment.
On the analytical side, this tool doubles as a powerful post-event resource. System operators can precisely trace historical faults, drawing insights from past incidents to tighten relay configurations and improve predictions. Overall, the solution not only enhances operational speed and accuracy but also supports continuous improvement and smarter grid management. Finally, the tools provide unique post-event analysis.
NEXT STEPS
GRE continues to enhance its technology to provide more precise analytics, leveraging weather, lightning, environmental, and other factors.



